
Simplified illustration of dual-globe lamp.
[Copyright 1999,2000 Frank Durda IV, All Rights Reserved. Mirroring of any material on this site in any form is expressly prohibited. The official web site for this material is: http://nemesis.lonestar.org Contact this address for use clearances: clearance at nemesis.lonestar.org Comments and queries to this address: web_reference at nemesis.lonestar.org]
However, this lamp design has a fundamental problem that prevents even distribution of light from all sides of the lamp: One of the electrical conductors is in the way.

In the shown illustration, the tungsten filament or the gas discharge arc
(depending on the lamp type) inside the inner globe is shown in yellow.
The electrical conductors are shown in red and green.

The problem is that in most designs, the lamp maker uses the most direct
path for the electrical conductor connecting to the end of the inner globe
furthest away from the screw base. This means that on one side of the
lamp, the electrical conductor will block most or all of the light from
the filament or electrical arc.
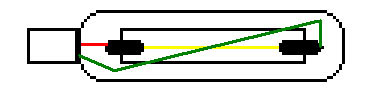
This alteration means that the electrical conductor is never running parallel to the filament or gas discharge arc, and the shadow is virtually eliminated. The added cost to making the lamp in this way is almost zero.
[Copyright 1999,2000 Frank Durda IV, All Rights Reserved. Mirroring of any material on this site in any form is expressly prohibited. The official web site for this material is: http://nemesis.lonestar.org Contact this address for use clearances: clearance at nemesis.lonestar.org Comments and queries to this address: web_reference at nemesis.lonestar.org]
Visit the nemesis.lonestar.org home page and index
![]()