SCSI-2 F/W
Questions on the Fast/Wide? Ask
ME
@8EFC.ADF - IBM PS/2 Fast/Wide SCSI Adapter
C8EFC.ADF - Init file for @8EFC.ADF
rev71upd.exe SCSI-2 Fast/Wide Adapter Firmware
Upgrade 7.1
corv77.exe SCSI-2 Fast/Wide Firmware
rev7.7
ibm2.exe F/W and OS/2 2.1 Fix '94
(ibm2scsi.add and ibm2m57.add)
scsi2fw.exe SCSI-2 F/W Support Diskette v2.0
193-294 SCSI-2 F/W Adapter/A
194-145 SCSI-2 F/W Adapter/A, SCSI-2
Differential F/W Adapter/A
SCSIFIX.ZIP Finally! A utility to alter the
number of sectors for a SCSI drive and convert them to a 3.94GB drive!
Bob Eager, you have answered a prayer!
SCSI-2 Fast/Wide Adapter/A
FRU 92F0160
Corvette Rear
LED Flash
Codes
Jumpers on
the Fast/Wide
MCA
Bus Controller Problems
Running Wide Devices
on Narrow Cables
Server
85 - Sharing External SCSI DASD Fails
RS/6000 Boot Support
Update Corvette
Flash
Maximum Number of Corvettes
Supported
80C188 vs. 80C186
PTC Function
68
pin Internal Connector
Drive
connector
68 pin External
Conductor
MCX
to HPDB68 Interposer
SCSI
device and adapter configuration flexibility
SCSI Device Order
Maximum SCSI Devices
Supported
Fast POST Consequences
ADF Sections
SCSI-2 Fast/Wide Adapter/A
Specs
Fast/Wide SCSI-2 Adapter/A
FRU
92F0160 "Corvette"
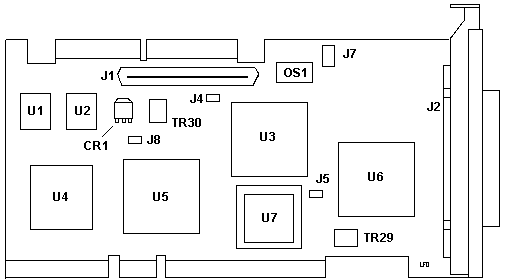
CR1 Mot 521
MOSFET(?) Int. Trmpwr
J2 Mini-C68
SCSI port
J4,5,8 Leave open. Not
used.
J7 Serial
port used during manufacturing
OS1 40MHz SMD Oscillator
TR29 PTC
on External SCSI bus
TR30 PTC
on Internal SCSI bus |
U1 61G3929, SCSI BIOS, Odd
U2 61G3930, SCSI BIOS, Even
U3 Internal SCSI ctrlr
U4 AMD N80C186-20
U5 61G2323
MCA Bus interface
U6 External SCSI ctrlr
U7 PLCC socket.
(unused on PS/2 or RS6K)10 |
U3 and U6 are
52G9307 (9314) on controllers made from about 9243 to 9340.
82G2645 (9352) on controllers made from about 9404 to 9512
Fast/Wide SCSI-2 Adapter/A
Rear

CR2 LED (flash
codes)
CR3 Mot 521 MOSFET? (termpwr external)
U8,9 89F7000 Term Network, external |
U10, 11 89F7000 Term Network, internal
U14, 19 Sony CXK581000AM-70LL
0 |
LED Flash Codes
- All versions of the SCSI-2 F/W adapter (Corvette
SE, DE, Enhanced/Turbo, and Integrated) have an onboard LED indicator
that provides general card status to aid in problem debug.
- At power ON, the LED stays lit until the SCSI
POST executes (RS6K, system LED=292). If the SCSI POST is successful, the
LED should turn off.
- If there is a hardware failure, the LED will flash
a failure code. The failing component is identified by the LED blinks,
a pause, then repeats the blinking code again, over and over.
Code Definition
Probable Causes
_____ _______________________________________ _________________
0 No error (LED turned off)
n/a
1 80186 ROM Test Failure
SCSI Controller
2 Local RAM Test Failure
SCSI Controller
3 FUSE Bad
Devices/Cable/Term
4 80186 Peripheral Test Failure
SCSI Controller
5 Local Transfer Bus (LTB) Test Failure
SCSI Controller
6 Undefined Error Condition
SCSI Controller
7 System Interface Control Chip Test Fail
SCSI Ctlr/IO Plnr
8 Internal SCSI Interface Test Failue
Device/Cable/TERM/Contrlr
10 External SCSI Interface Test Failure
Device/Cable/TERM/Contrlr
A blink code of 3, 8, or 10 may indicate a configuration
problem like a shorted cable or bad device, or duplicate SCSI addresses
on the same bus.
LED stays solidly lit after SCSI POST executes - replace SCSI
controller.
LED blinks during normal operation. If its non-periodic, it isn't
a problem. During normal operation the device driver may issue a command
reset to the adapter, when this occurs you will see the LED blink briefly.
- Example: If the LED blinks 8 times, this indicates
a bad internal SCSI bus. First, remove the internal SCSI cable from
the SCSI Controller. If the problem persists, replace SCSI Controller.
If not, add the cable and SCSI devices back (one at a time) until LED again
starts to blink.
J7 Pinout
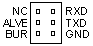 IBM's
patent info/Tech Discovery Bulletins, TDB
identifies the Burn/Alive/TXD/RXD as being used to flash certain components.
Basically, factory use only. IBM's
patent info/Tech Discovery Bulletins, TDB
identifies the Burn/Alive/TXD/RXD as being used to flash certain components.
Basically, factory use only.
Possible
MCA Bus Controller Problems (RS/6000 Specific,
but may affect PS/2s?)
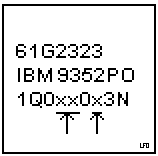 Some MCA bus controller chips, P/N 61G2323 (Malibu), can cause system problems.
The third line is the datecode. The following datecodes are suspect:
Some MCA bus controller chips, P/N 61G2323 (Malibu), can cause system problems.
The third line is the datecode. The following datecodes are suspect:
1Q010013N
1Q010023N
1Q03K023N
1Q04T003N
1Q06K013N
The entire datecode is not bad, but because of this,
the whole lot is suspect. If you have any of the symptoms below,
keep in mind the SCSI-2 F/W adapter may be the problem.
There are three types of symptoms you may see....
1) Checkstops (SIO BUS 0 or 1 PARITY)
2) System Hang/Unresponsive
3) DMA_ERR in the Error Log
Affected Controllers
SCSI-2 F/W Controller Type FRU p/n
U-location
* Integrated
52G4325 U60
MicroChannel SE
11H3600 U5
MicroChannel DE
11H7660 U13
Enhanced Microchannel DE 52G3380
U16
Note (*):
The Integrated SCSI-2 F/W controller is the one on the I/O planar of the
7012-380/390/39H and 7012-3AT/3BT/3CT systems.
Running Wide
Devices on Narrow Cables
I have pierced the veil of ignorance. I hope. The Corvette automatically
terminates it's end of the SCSI bus with termination networks on the back
side. However, some user intervention IS
required within System Programs.
Uli Link replies:
Not in terms of termination.
You must disable "wide messages" if you connect a wide
SCSI device to a wide SCSI controller through narrow cabling. During negotiation
both devices agree both can speak "wide". But the cabling cannot. So *no*
wide negotiation must happen.This is what disabling the "wide messages"
does. If you connect wide SCSI devices through wide cables all works automagically.
Some combinations of Narrow
and Wide devices on a Corvette
8EFCh "IBM PS/2 SCSI-2 Fast/Wide Adapter/A" or planar section
"Wide SCSI messages - External"
<"Enabled">, Disabled
Enable if you have a wide cable and a wide external device. However,
this should be Disabled.if you have a Wide SCSI device attached to the
adapter through a narrow (8 bits wide) external interface cable.
"Wide SCSI messages - Internal"
<"Enabled">, Disabled
Enable Wide - Internal if you have a wide cable and at least a wide
terminator (or wide device). Disable if you have a Wide SCSI device attached
to the adapter through a narrow (8 bits wide) internal interface cable.
Server
85 - Sharing External SCSI DASD fails
External SCSI DASD expansion shared between two
system fails when one of the systems is powered down. Systems affected
: 9585 0N* MCA SCSI-2 Fast/Wide controller card
On the 9585 0N* the trace on the solder (back) side of
the planar running parallel below resistor R351 must be cut. On the SCSI-2
F/W controller the trace running next to C30 on the component side of the
card must be cut. This trace runs from the fourth pin from the right on
the bottom of the larger IC next to the external connector.
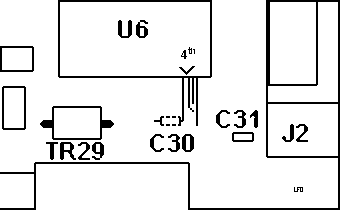
On the Corvettes in my possession, some have no trace at all from the
fourth pin, nor is there a C30 on the PCB. Others have it. YMMV.
Corvette Capabilities
The Corvette is a SCSI-2, 32-bit MCA 40MBps Data
Streaming bus master adapter with dual SCSI-2 16-bit, F/W channels (one
20MB/s internal, one 20MB/s external). The dual bus
of the adapter prevents access to internal DASD from the external port
and also allows the maximum cable length to be calculated individually
for each bus. Data transfer rates for 8 bit SCSI up to 10MB/s, 16
bit devices up to 20MB/s.
The Corvette supports SCSI Tagged
Command Queuing (TCQ), making it possible to send multiple commands to
the fixed disk, and the disk stores the commands and execute each command
in the sequence which will give optimal performance. Standard 8-bit SCSI
devices are supported using either asynchronous, synchronous, or fast synchronous
(10MBps) SCSI data transfer rates.
RS/6000 SCSI-2
Fast/Wide Boot Support
SCSI-2 Fast/Wide adapters available for the RISC/6000
are recognized as boot devices on all POWER2 and PowerPC systems.
They are not recognized as boot devices on POWER- based models. Any
devices attached to a POWER-based model via a SCSI-2 Fast/Wide adapter
may be used for storage but cannot be used as a boot device.
SCSI-2 F/W ADAPTER
(4-6, 4-7, 4-C) BOOT SUPPORT
MACH TYPE
MODEL PROCESSOR
SCSI-2 F/W
BOOT SUPPORT
7006
All
POWER PC 601/604 YES
7007 N40
POWER PC 601
NO (N/A)
7008
All
POWER RSC
NO
7009
All
POWER PC 601/604 YES
7010
All
XSTATION
NO (N/A)
7011
22x,23x
POWER RSC
NO
25x
POWER PC 601
YES
7012
32x,34x,35x,36x,37x POWER
NO
380,390,39H POWER2
YES
397
Power2 Super Chip YES
G30,G40
POWER PC 601/604 SMP YES
7013
52x,53x,54x,55x,560 POWER
NO
570,580
58H,590,591,59H POWER2
YES
595
POWER2 Super Chip YES
J30,J40
POWER PC 601/604 SMP YES
7015
930,950,97x,98x,R10 POWER
NO
990,R2x
POWER2
YES
R30,R40
POWER PC 601/604 SMP YES
7030
All
POWER2
YES
Update
Corvette Flash
From Uli Link over in Germany
Get Rev77.bin, it is the renamed - 8EFC3011.77M
from corv77.exe
Run rev71upd.exe It creates a bootable floppy
-
REV71 BIN
131,082 01-19-96 6:40p REV71.BIN
AUTOEXEC BAT
720 04-13-03 1:07p AUTOEXEC.BAT
README TXT
815 10-05-95 10:06a README.TXT
DOWNCORV EXE 2,479
08-31-94 6:16p DOWNCORV.EXE
REV58 BIN
131,082 09-22-93 3:50p REV58.BIN
SCSILEVL COM
928 03-24-93 5:31p SCSILEVL.COM
COMMAND COM 48,006
10-25-91 12:00p COMMAND.COM
DOWNNEW EXE
2,479 08-10-94 9:53a DOWNNEW.EXE
Copy Rev77.bin to a:, Edit a:\autoexec.bat:
@echo off
//--------------------//
@echo on
pause
downnew rev77.bin <<<<<<
rename the rev71.bin to rev77.bin
@echo off
//---------------------//
You can use "downcorv.exe" instead of "downnew.exe" "downnew.exe"
checks for flashing only newer fw into corvette. "downcorv.exe" is even
able to downgrade.
If you flash the DOS way, the new fw level is NOT recognized
by AIX. To flash a PS/2 corvette in a RS/6000 rename 8EFC3011.77M to 8EFC0001.77M.
Now the fw level 077 is recognized by AIX. The adapter still will work
in a PS/2 and can be downgraded back to 071 or even 058.
Tested with 3 corvettes in RS/6000 C10 and 2 Lacunas. No
problems so far. But no problems before flashing, too.
How Many is Enough?
Tim Clarke uttered this after a pint of warm beer:
All **IBM** SCSI CBIOS-flavour (i.e. *not* FD MCS700 OEM)
will share IRQ14 and you only need one BIOS ROM enabled to drive multiple
adapters. So, for example you *should* be able install (in the same slot-type,
please) IBM F+W SCSI-2 "Corvette", IBM SCSI w/cache ("Spock") and IBM SCSI
w/o cache ("Tribble") in the same PS/2. No naughties like AHA1640, Storage
Dimensions unless you disable their BIOS ROMs and assign a different IRQ.
OS Limits
Not all Micro$haft products support multiple IBM SCSI adapters
gracefully. W9x cannot handle shared IRQs and will drop into MS-Doze (In)compatibility
mode. Win NT handles the shared Interrupts. OS/2, Linux and
many unixes support shared Interrupts.
80C188 vs.
80C186
Older adapters (SCSI, SCSI w/cache) use an 80C188-16 microcontroller
as busmaster-CPU, the Fast/Wide uses an 80C186-20 busmaster CPU.
Both CPUs however are integrated CPUs with 2 8-bit parallel-ports,
the -188 has 8-bit external data-path, the -186 has 16-bit external data-path
and slightly different (enhanced) command set.
PTC Function
There is one PTC for the internal SCSI bus and another
for the external bus. The PTC protects the SCSI bus from high currents
due to shorts on the cable, terminator, or device. It is highly unlikely
that the PTC resistor can be tripped by a defective adapter.
A fault (short circuit) causes an increase in PTC resistance
and temperature. The increase in resistance causes the PTC resistor to
halt current flow. The PTC resistor returns to a low resistive and low
temperature state when the fault is removed from the SCSI bus or when the
system is powered off. Wait 5 minutes for the PTC resistor to fully cool,
then reset.
MF-SM Series MF-SM150
PLCC Socket on Fast/Wide
The PLCC Socket U7 was possibly to provide a RS6000 Bios, and
the jumper J5 might have been to enable it. Documentation for the RS6000
says that the PLCC socket is unused.
Jumpers on Fast/Wide
The results of shorting the jumpers ranged from no difference,
slight performance hit (%10 overhead increase) or a system-halting error.
Leave them off. RS6000 documentation says the jumpers are to be left open.
J4 grounds out pin 33 of
the MCA Bus Controller, 61G2323. Purpose unknown.
J5 Purpose unknown.
J8 grounds out Pin 1 of both
U1 and U2. Resembles J6, Boot Block Enable on DFW.
68
pin Internal Connector on F/W SCSI Adapter
This is a "mini-Centronics" plug. The ANSI moniker for it is
a "P" plug. Also seems to be used for SCA drives... Hmm...
AMP (and Tyco) # 1-557089-2
Looks like THIS
or if you want the page go HERE
Newark Electronics 97F8813
CHAMP. 0.050 I Series Interface Connectors For VMC Applications: 68-Position
Designed for 30 AWG solid conductors on .064mm (.025")
centers. For details, look HERE
Molex 71660i Molex part 15-92-3068
1.27mm (.050") Pitch
EBBI™ 50D - Receptacle, Vertical, IDT 71660i Looks like THIS
Terminates to 30 AWG solid or stranded.025" ribbon cable
or laminated discrete wire cable
Drive connector
The 68 pin crimp-on device connector. Dalco 59611
$4.25

68 Pin External Conductor
I'll be darned if I know who made the leaf connector.
From my lurking about, the peculiar connector is called the "MCX" and is
made from unobtanium.
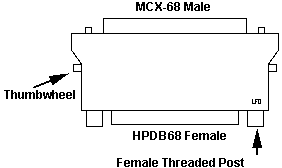
Using HPDB68
Cables with MCX Ports
The C68 or MCX port is refreshingly rare. IBM did have
some smarts when it made a handy-dandy adapter, "Interposer 68 Ribbon to
68 Socket", P/N 50G0460. Mine is made by Amphenol with a date of 06/97.
Use of this interposer is simple. Use the thumbwheels
to fasten the interposer onto the F/W adapter. Screw on the HPDB68 socket.
Power on and compute.
SCSI
device and adapter configuration flexibility
Systems with the enhanced SCSI device and adapter support
allow up to 8 IBM PS/2 SCSI adapters of any type to be installed in a single
system. The maximum number of SCSI devices which many be configured in
these newer systems has also been increased from 60 to 120. However,
other factors, for example, the type of devices (optical, etc.), cooling
requirements, or power consumption of the devices may limit the number
for a particular system.
SCSI Device
Order
SCSI device logical ordering and hard drive letter assignment
(e.g. C:, D:) sequence is determined by the SCSI adapter slot numbers,
internal or external SCSI bus connection, and SCSI ID of the connected
devices.
Adapters are scanned for SCSI devices beginning with the
SCSI adapter in the lowest numbered slot. Devices connected to the
same adapter are logically ordered according to device SCSI IDs in order
from 7 to 0 and then from 15 to 8 according to the priority scheme defined
by the SCSI standard. Devices connected to a SCSI-2 Fast/Wide adapter's
internal bus connector are ordered logically before devices connected to
the external bus of the same adapter.
Maximum SCSI
Devices Supported
Wide SCSI devices support 16 possible SCSI ID values.
The adapter uses one these values; therefore, the SCSI-2 Fast/Wide adapter
can connect up to 15 fast and wide devices internally or externally in
any combination using the remaining ID values. Narrow SCSI devices
support 8 possible SCSI ID values; therefore, up to 7 narrow SCSI devices
can be connected to the internal or external SCSI busses in any combination
using the remaining ID values. Wide and narrow devices may be mixed
on the same internal/external bus by using the proper combinations of SCSI
bus cables, terminators, and/or SCSI connector convertor adapters.
NOTE: Use of a 8 bit
(Narrow) cable forces the controller to default to only 7 devices supported
on that port, even if all devices on that cable are Wide.
Fast POST Consequences
Some newer systems also provide a FAST POST option which
may be selected from the system configuration menu or from the IBM logo
screen. When this option is selected, the system will not check for
the presence of newly added SCSI devices unless F1 is also pressed while
the IBM logo is displayed. Newly added SCSI devices will not be configured
nor will an error occur if the fast post option is chosen as the default.
To access the system configuration program, press F1 while the IBM logo
screen is displayed to configure the new SCSI device(s) initially.
ADF Sections @8EFC.adf
4/10/95
I/O Address
I/O address for the adapter. Each adapter must have a
unique address range.
<3540-3547>, 3548-354F,
3550-3557, 3558-355F, 3560-3567, 3568-356F, 3570-3577, 3578-357F, 3578-357F
DMA Arbitration Level
Arbitration level used by the adapter to transfer data.
<C>, D, E, 8, 9, A, B,
1, 3, 5, 6, 7
SCSI Adapter Address (ID)
SCSI ID of the adapter. Usually ID7, unless you have specific
requirements.
Adapter IDs available are: <7>,
6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0
Move Mode Support
Enable or Disable Micro Channel Subsystem Control Block
Move Mode This is the second mode of SCBA (first is locate mode) which
permits the system processor to move the subsystem control blocks to the
adapters directly.
<Enabled> or Disabled
Wait State Support
Enable or Disable Bus Master wait states. If the target
expansion card is an older card, it may not be able to process commands
or data from the busmaster fast enough, and when queried by the busmaster,
it replies with "not ready". By inserting a wait state, the slower card
has more time to signal "ready". Enabling wait states can slow your busmaster
down.
<Disabled> or Enabled
Data Parity Exception Handling
This Adapter can generate and detect data parity on Micro
Channel. Data parity must be supported on both ends of an across-the-bus
transmission in order for this error detection process to be effective.
A data parity enable (-DAPAREN) bus line to the system and other expansion
boards is enabled when data parity is being used. If the System does not
support Data Parity Exception Handling, this feature will always be disabled.
<Enabled> or Disabled
Selected Feedback Return Exception
Whether a busmaster will report errors detected in the
select-feedback-return process.
When enabled, the busmaster monitors the selected feedback
return and card-selected feedback buslines. The return line tells the master
that it's target expansion board is responding properly to being addressed
for a read or write operation. If the bus master does not recieve this
signal (and SFR has been enabled) it may mean that the expansion board
is not operating properly or that the signals themselves are not properly
traveling across the expansion bus. This error causes the master to immediately
halt the transfer in progress and notify the host system of the error using
an interrupt. NOTE: The SFR must be
ignored for PC compatibility. If the System doesn't support the Selected
Feedback Return feature, it will always be ignored.
<Enabled> or Ignored
100ns Streaming Data Transfer Support
This provides better performance. It will always be disabled
if the system doesn't support it.
<Enabled> or Disabled
Target Mode
Target mode should be disabled only if this system is
sharing SCSI devices with another system and there are more than 15 devices
to be shared. Only 15 devices can be configured on each adapter.
When
target mode is enabled, this adapter appears as a processor device on the
other system and unless you have specialized software that can communicate
between the two systems through these processor devices (peer-to-peer communication),
there is no advantage in having
target mode enabled. When target
mode is disabled, this adapter does not appear as a device to the other
system, and one more device can be shared by the two systems. If
your system is not sharing any SCSI devices with another system on this
adapter, it does not matter whether you enable or disable target mode.
<Enabled> or Disabled
SCSI Disconnect
Disconnect is a SCSI-bus procedure in which a device logically
stops communicating with the adapter during certain operations and then
reestablishes communication with the adapter when the operation is complete.
Disconnect should not be confused with the 'Presence Error Reporting' option
for a device in 'Set and view SCSI device configuration.' If you
are using an operating system that is single-threaded and issues commands
to only one device at a time (such as DOS or Win95),
disabling SCSI disconnect might result in a slight performance improvement.
If your operating system is multi-threaded (such as OS/2), disabling SCSI
disconnect will degrade the performance of the SCSI subsystem.
<Enabled>
or Disabled
Fast SCSI - External
If you have Fast SCSI devices attached externally, enabling
Fast SCSI improves performance :
- One external SCSI device enclosure model 3511.
- Up to three external SCSI device enclosures model 3510.
- Any external configuration where SCSI cable length isn't >
3 meters.
<Disabled> or Enabled
Wide SCSI messages - External
This should be 'Enabled' unless you have a Wide SCSI device
attached to the adapter through a narrow (8 bits wide) external interface
cable.
<Enabled> or Disabled
Wide SCSI messages - Internal
The setting for this should be 'Enabled' unless you have
a Wide SCSI device attached to the adapter through a narrow (8 bits wide)
internal interface cable.
<Enabled> or Disabled
Internal/External Bus Mode
'Separate', SCSI devices on external SCSI bus connector
can have the same SCSI ID setting as other SCSI devices connected to
internal SCSI bus connector on the same adapter.
'Combined', all devices connected to this adapter
must have unique SCSI ID settings regardless of which SCSI bus connector
is used to attach the devices. Default is 'Separate' unless you are
using an operating system device driver that does not support independent
operation of the internal and external SCSI busses on the adapter.
<Separate> or Combined
System Determined
ROM Address Range
Address of the 32K block of memory assigned to the adapter.
Only one SCSI Adapter will have the ROM assigned, and any other SCSI Adapter
installed will share that address range.
ESDI Requirements
If the ESDI adapter is also installed, then the address
of the SCSI adapter must be greater than the ESDI adapter address.
SCSI-2 Fast/Wide
Adapter/A Specs
| SCSI type |
SCSI-2 Fast/Wide |
| SCSI bus path / speed |
16 bit / 20 MB/sec |
| I/O bus path / speed |
32 bit / 40 MB/sec streaming |
| I/O features |
Streaming data transfer
Address parity and data parity |
| RAID levels |
None (use software) |
| Tagged Command Queuing |
Yes |
| Processor |
80C186 at 20 MHz |
| Size |
Type 3 (short) |
| Channels |
Two (one internal/one external) |
| Connectors |
Two internal SCSI-1 or SCSI-2 cabling
50 pin edgecard and 68 pin mini C68
(only one active);one external C68 |
| Devices supported |
7 narrow or 15 wide per adapter
15 on Server 500 on one or two channels |
| Cache std / max |
0 KB / 0 KB (128 byte buffer) |
9595 Main
Page
|

 Some MCA bus controller chips, P/N 61G2323 (Malibu), can cause system problems.
The third line is the datecode. The following datecodes are suspect:
Some MCA bus controller chips, P/N 61G2323 (Malibu), can cause system problems.
The third line is the datecode. The following datecodes are suspect:


