|
IBM Token-Ring Network 16/4 Adapter/A
@E001.ADF - IBM Token-Ring Network 16/4 Adapter/A
(Tropic based version 2.01!)
E000.DGS - Diags
TRM164.EXE Drivers/Diagnostic/Option
disk v2.0 (includes ADF ver 2.01 and DGS)
Many adapters use "E001" adf. But there are different versions of the adfs
to choose from.
187-076 IBM Token-Ring Network Adapter/A
(4Mbs)
188-202 IBM Token-Ring Network 16/4 Adapter/A
(Short and Long 16/4)
190-004 IBM Token-Ring Network PS/2 Model
P70 386 Adapter/A (4Mbs)
190-090 Token-Ring
Network 16/4 Trace and Performance Adapter/A
290-284 IBM TR Network
16/4 Trace and Performance Program
Short 16/4 Token Ring
Adapter (74F9415 or 74F9321)
02G1394ESD
vs. 50G6144ESD
Tokin'
Madness
16/4 Long Token Ring
Adapter
53F7748
16F1144
Short 4MB Token Ring Adapter
25F7540
Identifying the Tropic
Chipset
OEM Tropic chipset list
Registers on Screen?
Adapter fails to
insert on ring
Promiscuous Copy and
Promiscuous Mode
Trace and Performance Adapter
Hack (feel the urge to burn?)
ADF Settings
Short 16/4 Token
Ring Adapter (74F9415 or 74F9321)
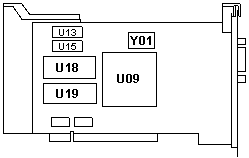
|
U09 02G1394ESD or 50G6144ESD
U13, 15 Toshiba TC55329J-25
|
U18 74F9686 /
91 OR 60G2484 / 93
Y01 32.000MHz |
Most short 16/4 have the RPL-code integrated in the ROM-code - the
4Mb/s and the long 16/4 adapters have a separate ROM for it - and the chip
needed to be purchased separately.
o 16/4 megabits-per-second adapter data rate -- program selectable
o 64KB RAM on card
o Larger maximum frame size - At 16Mbs - 17,997 bytes, 4Mbs 4501 bytes.
o RAM paging - software can access all 64KB of RAM, but only uses 16KB of PS/2 memory space
o Maximum # of link stations increased from 64 to 254
o Early Token Release at 16 megabits per second
02G1394ESD vs. 50G6144ESD
Win95 can detect the difference between the two. Install a 16/4 with
main chip 02G1394ESD. W95 is happy. But install a 50G6144ESD, up comes the
familiar "Your IBM 16/4 Token Ring is not set up correctly..."
W95 will continue to load and the TR works on an 8228. Must
be the chipset is close enough to complain about, but also close enough to
work.
Tokin' Madness
I got a few more short 16/4s. I noticed some (to me) interesting
factoids. The 02G1394ESD chipset cards' bios
chips do not change their dates. The 50G6144ESD
have two sets of bios dates, some are 1990 and some are 1993. I have one
50G6144ESD card that has the bios chips
from the 02G1394ESD card.
Postulate- The 02G1394ESD chip
is OK, but the 50G6144ESD had a problem, they
issued a new bios for it. They even tried the bios off the 02G1394ESD. I don't have a large enough population
to derive a high correlation, but... My wild SWAG is as good as yours...
16/4 Long Token
Ring Adapter 53F7748 / 93F0331
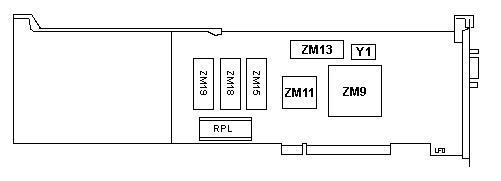
ZM9 51F1439ESD/63F7704ESD
ZM11 25F7335
ZM13,15 M5M5256BP-10L
or
CXK58257AP-70L |
ZM18 25F9524
ZM19 25F9523
Y1 32.0000 MHz
RPL RPL |
16/4 Long Token
Ring Adapter 16F1144
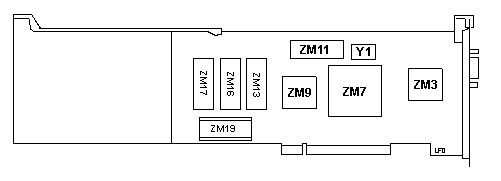
ZM3 64D7274ESD
ZM7 02F8442ESD
ZM9 25F7335
ZM11,
13 NEC D43256AC-19LL |
ZM16 25F9532
ZM17 25F9531
ZM19 25F9523 RPL
Y1 32.0000 MHz |
Differences between the 53F and 16F adapters are the
addition of a 64D7274ESD and different ROM (25F9532 and 25F9531). They are
basically the same - however the one with the 64D7274 at ZM3 is the later
revision. This chip contains the output drivers and some "corporate logic",
which was the 2 14-pin ICs on the elder version (ZM1 & ZM4).
The P/N for the RPL-ROM is 25F8923 by the way.
o 16/4 megabits-per-second adapter data rate -- program selectable
o 64KB RAM on card
o Larger maximum frame size - At 16Mbs - 17,997 bytes, 4Mbs 4501 bytes.
o RAM paging - software can access all 64KB of RAM, but only uses 16KB of PS/2 memory space
o Maximum # of link stations increased from 64 to 254
o Early Token Release at 16 megabits per second
4MB Token Ring Adapter
25F7540
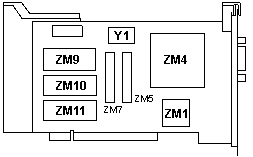
ZM1 25F7335
ZM4 51F1439ESD
ZM5, 7 Mitsubishi M5M5179P-55
ZM9 25F9158, Even
|
ZM10 25F9157, Odd
ZM11 BIOS (RPL)
Y1
32MHz
0
|
With the infamous Tropic chipset
16KB of RAM
Identifying the
Tropic Chipset
Hi Louis !
>Is the 51F1439ESD and 25F7355 the Tropic chipset?
If the card-ID = E001 (or E000 for the 4Mb/s) then - Yes. This chipset
is also used by all E000 / E001 compatible cards from Madge, Compex, Hypertech,
Kingston etc. pp. ... some cards use different card-ID however.
IBM came "out of the TROPICs" for MCA with the LanStreamers
(MC16 - 8FA4/ MC32 - 8FA0 & 8FA2). The TR Server Busmaster adapter (8FC8)
bases mainly on the Tropic architecture as far as I know.
OEM TROPIC chipset
list
Listed below is the TROPIC chip set that IBM licensed from National Semiconductor.
DP8025 Token Ring Interface Controller
DP802511 TROPIC RAM Relocation Register Decoder
DP802512 Upper Memory Decoder
DP802513 Memory MEMCS-16 Signal Decoder
DP802514 TROPIC REEF
DP802515 TROPIC PELE
The DP802514 and DP802515 are Microcode ROMs for the TROPIC
Token-Ring Network Controllers and they feature an interface that is compatible
to DP8025 Interface Controller to allow direct interfacing without the use
of GLUE logic.
Peter sez:
If you look at the Madge "True Blue" 16/4 card you will find
the same silver capped NatSemi chip there. Card has ID E001 - and works with
the same "Tropic" drivers under Linux. NatSemi was a second source manufacturer
of the Tropic chipset for quite some time. Other customers were e.g. Hypertec
in Australia, which used IBM and NatSemi chips. At least I have seen Hypertech
E001 cards with both sorts of chips.
In the pictures database there is a Madge TR with the NatSemi
and a Hypertech (long card) with the IBM chip. Later -on the Auto-TR 16/4-
IBM switched to an all-plastic chip.
David Beem sez:
My "Networking the Desktop, Cabling, Configuration, and
Communications" (Deni Conner/Mark Anderson, Academic Press, 1995) explains
the various TR chipsets in a couple of paragraphs. The NS chip is refered
to in the second:
"Texas Instruments (TI) announced an agreement with IBM
to develop a token ring chipset called the TMS380 based on the IBM token-ring
specification. This chipset had technological and performance advantages over
the IBM chipset that allowed increased data buffers for data transfer and
also allowed direct memory access (DMA) transfers, in which an onboard controller
managed access to memory. Later, TI enhanced the TMS380 chipset to accomodate
16Mbps token-ring networks, resulting in the TMS380C16. Recently [to when
the book was written], TI announced an advanced token-ring chipset using
the TMS380C26 chipset, which integrates more functionality than the previous
two.
While the TI chipset is 100-percent compatible with the
IEEE 802.5 and 802.2 token-ring specifications, it is not 100-percent compatible
with IBM's LLC protocol implementation. As a result, IBM developed the Token-Ring
Protocol Interface Controller (TROPIC) chipset for third-party vendor use,
ensuring register-level compatibility for all IBM applications. Marketed by
National Semiconductors under licence from IBM, TROPIC manufacturers include
vendors such as Madge Networks, Proteon, Thomas-Conrad Corp., Cabletron Systems,
and 3Com.....".
Registers on Screen?
This is new- I got a few lines in the upper left eigth of the screen.
They were registers- AX, BX... They didn't change... There was a top line
with an ET that actually counted the seconds... Up to 26 by the time I gave
up on rebooting...
Peter-
That's a TR adapter trying to RPL..... check startup sequence.
Memory
It has 64 KB of random access memory (RAM), of which 63.5 KB are
available for use by an application program and 512 bytes are reserved.
Adapter fails
to insert on ring
A Token-Ring adapter may fail to insert on the ring due to
adapter congestion. Adapters entering the ring send a request to the Ring
Parameter Server (RPS) address to learn ring parameters, such as ring number.
If the RPS exists on this ring, which is usually the case only if the ring
is bridged to another segment, this RPS request frame returns to the originating
station with the Address Recognized Indicator (ARI) set; ARI set
informs the inserting station that the RPS exists on this ring and that the
station should wait for the RPS response before completing its insertion on
the ring. The RPS returns its response to the inserting station as
a normal Token-Ring frame. If the inserting station's adapter has begun
to experience significant congestion by this time, it may not be able to
process the frame. The adapter driver then will stop the adapter's insertion
because the adapter was unable to process the RPS response.
This problem is more likely to occur on multistation access
units (MAUs) with electronic relays that do not disturb the ring
during an adapter insertion; the adapter may have to wait seven seconds
to participate in the neighbor notification process. In units without
electronic relays, the relay disturbance causes the active monitor
to start a new neighbor notification process and the adapter does not have
to wait as long to insert. The longer insertion time increases the probability
that the adapter will become congested.
The 802.5 Standards Committee recommends that the RPS send
two frames to the adapter: one normal frame and one frame with the express,
buffer-bits set. The inserting adapter will then copy the express frame
into its express buffer. This information is documented in the errata
sheets from the 802.5 Standards meeting V.
Promiscuous Copy
and Promiscuous Mode
NOT supported on the 16/4 Token-Ring Network Adapter/A
with RPL, 16/4 Token-Ring Network Adapter/A or the Token-Ring Network Adapter/A
Trace and Performance
Adapter
I thought these were special adapters. Turns out that it's
just a special BIOS for the short and long 16/4 TR adapters...
From Peter
You need the two .BIN files for burning two Eproms. These replace
the two Eproms on the 16/4 card. The "analyzer" machine needs to run a generic
DOS with the modified adapter installed.
Then extract the TAP20.BIN ... at the C:/ Dos-prompt
type TAP ... then "Measure Ring Performance" - enter any file name for storing
the performance data, [ENTER], then select "Start measuring" from the menu
... and if you did it all right you get a nice bar graph with the TR network
load. Mine never reaches values over 65% - even when I have all workstations
running and do large copy and backup jobs.
There are other functions as well. You could build a
"traffic matrix": simply spoken "who talks with whom ?" - the program shows
the burn-in adresses (these 12-digit codes burned in the adapter) - here
it pays to overwrite these internal adresses with own ones ... my server
for example has 4000 0001 CAFE (hex numbers only).
Or having a list which computer has which burn-in adress. WINIPCFG
(under 95/98) shows the burn-in adress, some cards have stickers at the
rear (LanStreamer, modern cards).
Hmmm....I am not quite sure at the moment if you need any
of the DOS LAN support drivers (DXMA0MOD.SYS / DXMC0MOD.SYS / DXMT0MOD.SYS)
in your CONFIG.SYS. My P70 has at least the DXMA0MOD.SYS ... but the TAP
opens and closes the adapter during operation.
3 files.
1. TAP20.ZIP (The software, includes ROM files)
2. TAP164O.BIN (Odd Eprom, 27C256-20, Checksum 518E)
3. TAP164E.BIN (Even Eprom, 27C256-20 Checksum 9B14)
I tried them with the "long" 16/4 and the two short ones (with and
w.o. RPL). Currently they are running with a 93F0179 - which is the short
16/4 with RPL.
ADF Settings AdapterID E001h " IBM Token-Ring 16/4 MC Adapter,
ver2.01"
Primary or Alternate Adapter
Up to two Token-Ring Network adapters may be installed
in a computer, either as Primary, (accessed at 0A20 through 0A23),
or Alternate (accessed at 0A24 through 0A27). If one Token-Ring Network adapter
is installed, it may be either Primary or Alternate. If two are installed,
one must be Primary and the other Alternate.
< "Primary" 0A20h - 0A23h>,
"Alternate" 0A24h - 0A27h
Adapter Data Rate
The data rate must be set to the same rate (4 or 16 Mbps) as
the Token-Ring Network to which you are connecting the adapter. The 4MB TR
card doesn't have a choice, it's 4MB only. If you attach a 4MB adapter to
a 16MB network, the network will automatically drop to the 4MB/sec rate.
In short, don't mix speeds!
<"16 Mbps">, 4 Mbps
ROM Address Range
There are 12 possible 8K blocks of memory that can be assigned
for accessing the ROM area of the Token-Ring Network adapter. The preferred
ROM address is CC000-CDFFF.
RAM Size and Address Range
There are 30 possible blocks of memory that can be assigned
for accessing the RAM located on the 16/4 Token-Ring Network adapter. The
preferred RAM Size and Address Range for the adapter, which allows RAM Paging,
is: 16 KB / D8000-DBFFF.
Interrupt Level
This Token-Ring Network adapter can operate on one of four
interrupt levels: 2, 3, 10, or 11. The preferred interrupt level is
2.
<"Interrupt 2">, 3,
10, 11"
Adapter Media Type Selection
This adapter supports two media types, STP and UTP. If
you select STP, your LAN cable must be attached to the 9-pin D-Shell connector
on your adapter. If you select UTP, your LAN cable must be attached
to the RJ-45 jack on your adapter. If your LAN cable is not attached
to the selected media type, the adapter will exhibit a LOBE MEDIA FAILURE.
If your Token-Ring adapter only has the 9-pin D-Shell connector, the Media
Type Selection will be ignored.
<"STP">, UTP
Enable or Disable RPL
This adapter can be used in a medialess system by enabling
the Remote Program Load (RPL) or vice versa when chosing DISABLED.
BEWARE: if RPL is ENABLED,
some high level software programs (eg. some server software) may require
that the adapter be configured as the primary adapter. If your Token-Ring
adapter has a separate RPL module socket, the Enable or Disable RPL option
will have no effect
<"Enabled">, Disabled
9595
Main Page
|