|
TR Network 16/4 Busmaster
TRMBUSM2.EXE Drivers/Diags/Option v3.0
(1.44MB version)
@8FC8.adf (rename
to @8FC8.adf) @
bk8r2000
T-R Network 16/4 Busmaster Server Adapter/A Interface HERE
Token-Ring Network 16/4 Busmaster
Another Version?
16/4 Busmaster Repressed Memories
Error Messages
Calculate MAXTRANSMITS and MINRCVBUFFS
ADF Sections
Token-Ring Network
16/4 Busmaster
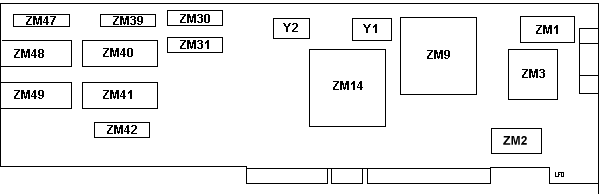
ZM1 39F6511
ZM2 39F6511
ZM3 64O7274ESD
ZM9 51F1439ESD
ZM14 74F8357ESD
ZM30 39F7825 3021
ZM31 39F7825 3401
ZM39 5C6401-35 |
ZM40, ZM41 SRM20256LC10
ZM41 SRM20256LC10
ZM42 74F8652 X031
ZM47 5C6401-35
ZM48 SRM20256LC10
ZM49 SRM20256LC10
Y1 32.00000 MHz
Y2 40.000 MHz |
Another Version?
I have just picked up another 16/4
Busmaster (RS6K, 2-2). Looks to be an improved version. Maybe. Appears
to have been made in 1995
ZM9 63F7704ESD.
ZM30 39F7826 9519 PEH
ZM31 39F7826 9519 PEH
ZM42 93F1272 9511 PCO
Unfortunately, the 32 bit portion is still pretty bare.
Still a 16MB card?
16/4 Busmaster
Reminicience
From Peter
Hi Louis !
>Peter, can you shed some light on this? I know the TRB was dropped.
Can't find an eca on it other than the messed up fairness setting in the
downlevel options disk.
Uh ... we are talking about the TR 16/4 Busmaster Adapter
/A (ID: 8FC8) here, right ? Well - that thing was developed originally
for the RS/6000 and sold as "Hi Performance TR Adapter" there ... and was
very, very shortlived (in terms of IBM) in the PS/2 world, because it was
true crap.
Technically its' based on the "Tropics" chipset - or a
further dead-end-street developement of it, which was discontinued for
the much better LAN Streamer adapters.
>Why won't the bus master run when more than 16 mb of memory is installed
in a server? Under Netware 3.12, the adapter NLM won't load because it
says that it can't reserve memory space below the 16 meg boundary.
Were these adapters limited through DMA to run only in the older machines?
The ADF lists NODMA ... and I do know absolutely nothing
about No- Well .... the card has been designed to work under OS/2 - and
did as far as I can tell. We had a few in 95s in the early 90, but they
had no real advantage against the older Tropics 16/4 ... so they got the
moving-papers after the Lanstreamer MC32 entered the stage. The 16/4 BM
has been announced for a few machines only IIRC. Have no idea why it should
choke with above 16MB - which is a 24-bit DMA boundary. The Mod. 80 cannot
- for sure - it is known for problems with memory over 16MB. The modern(er)
9595 should be capable to handle it.
If you look at the TR 16BM you will find that the 32-bit
portion of the MCA connector is almost empty: No D16 - D31, no A24 - A31.
The signals at that part are for card selection / feedback (-SFDBKRTN at
pin A64) and adress parity (-APAREN, APAR(0)-(2) - but not APAR(3) for
the address bits 24-31). This adapter is basically a 16-bit card - and
that would explain the misbehaviour. Since the physical interface covers
only 24 address bits it is limited to 16MB memory - and the NLM will have
to use the "lower 16" for all stuff.
I -personally- would recommend getting rid of the card,
install a generic TR-16/4 "Tropic" instead, which has a much simplier driver,
does not care for address parity and can be used on machines with over
16MB (proven..).
About the "Token Ring 16/4 Busmaster Server Adapter" (8FC8)
- often referenced as "High Performance Token Ring 16/4 Adapter": that's
a parallel developement originally intended for the RS/6000. It is largely
based on the "Tropic" technology but uses DMA (the Tropic don't) and different
I/O adresses. It is limited to 24-bit adressing / 16-bit data bus. It causes
a lot trouble on machines with over 16MB RAM. It's a long card with *two*
large and one medium-sized silver capped chips and very easy identifyable
through the four 32K SRAM chips (61256 or compatible in 2 x 2 arrangement)
at the card front end. This card is useless under almost any OS .
Error Messages
LT40009
Error message LT40009 on the IBM 16/4 Token-Ring Network Busmaster Server
Adapter/A. This may be caused by the busmaster receiving
a frame with a routing field larger than 18 bytes. This occurs when the
frame being received has traveled accross 8 or more bridges. Setting the
hop count to 7 on all bridges will prevent this problem.
You should also update the IBMTRBM.OS2 device driver to
the latest version, as least 3.00.18, to prevent this problem. It can be
found in the device driver package located at the adapter's support page
http://www.networking.ibm.com/support/trbusmstr
NetWare requesters/servers drop sessions across
Cisco routers
Symptom
When an idle workstation is being queried by a NetWare server with
IPX watchdog packets, the Cisco router does not update the timestamp in
the RIF cache. Because the router then does not know where to send the
watchdog packets, it sends out an LLC XID test frame to obtain a route.
Stations having either non-Turbo, shared-RAM adapters
with on-board LLC or DMA/busmaster adapters that have an 802.2 protocol
loaded in the workstation respond to this frame, but stations with DMA/busmaster
adapters with no 802.2 protocol loaded do not respond.
The NetWare server continues to send IPX watchdog packets
with no response and eventually the server terminates the connection.
Fix This problem can be resolved
by performing any of the following corrective actions:
Turn off multi-ring support for the Cisco
router. This action is acceptable if the Cisco router is routing but not
bridging. Set the Cisco RIF table addresses to the value Static, which
prevents the router software from timing out the RIF cache entry.
This action may or may not be acceptable,
depending upon the network Configure the NetWare server watchdog packets.
On NetWare 4.1, the watchdog packets default to first packet after five
minutes idle; the parameter value can range from one minute to 14 days.
Upgrade to 10(3) level of software for the
Cisco router. This action could require a hardware upgrade for older routers.
Configure an active LLC 802.2 protocol driver
in the workstation:
Win95, Win98,
NT - Load the NetBEUI and MSDLC32 protocols.
DOS/Win 3.X
- Use LAN Support Program or IBM LAN Client with the LLC protocol configured.
OS/2 - Configure
the 802.2 protocol (LANDD) in MPTS.
NetWare Server
- Use Novell's IEEE8022.NLM.
If you are using the IBM Turbo 16/4 Token-Ring
Network ISA Adapter , the IBM Turbo 16/4 Token-Ring PC Card, the IBM Turbo
16/4 Token-Ring PC Card 2, or the IBM Auto Wake 16/4 Token-Ring Network
ISA Adapter, specify the NOSHALLOWMODE parameter for the device driver
being used.
Calculate
MAXTRANSMITS and MINRCVBUFFS parameter
MAXTRANSMITS
Use the following formula to compute the maximum value:
H(i) = RCVAREA(i) + ALLOCSIZECB(i)
A H(i) value should be computed for each IBM Token-Ring Network 16/4
Busmaster Adapter, and the sum of all H(i) values must be less than 1 MB.
(i) means individual.
RCVAREA
Receive area for each adapter:
RCVAREA = MINRCVBUFFS x SIZWORKBUFF
ALLOCSIZECB
Control block area for each adapter. Must be less than
64KB
ALLOCSIZECB = 334 + (142 x MAXTRANSMITS) + (20 x MINRCVBUFFS)
ADF Sections
Adapter Data Rate: Operates
at two different data rates: 4 Mbps or 16 Mbps. The adapter data
rate MUST be set to the rate of the Token-Ring Network LAN segment to which
you are connecting the adapter.
Interrupt Level Operates on
one of eight interrupt levels: 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 10, 11, or 12.
The preferred interrupt level is 2, but the adapter can operate on any
of the eight levels if necessary.
I/O Address An adapter can
operate at any of eight I/O address ranges (86A0 - 86AF to F6A0 - F6AF).
If more than one adapter in your computer is used, each adapter must be
assigned a separate I/O address range.
Arbitration Levels Select one of
fourteen arbitration levels: 0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, A, B, C, D, or
E. If more than one adapter is used in your computer, each adapter must
be assigned a separate arbitration level.
Fairness: Operates with or
without arbitration fairness.
Bus Release: During a Micro
Channel DMA operation there are two different ways of releasing the bus
after the Preempt signal. After a Preempt occurs the bus can be released
either immediately or by the maximum time allotted by the Micro Channel
architecture. The best performance is achieved if this adapter is
allowed to continue for the maximum time allowed.
Early Token Release This function
is only applicable at the adapter data rate of 16 Mbps. The best
performance of the network at 16 Mbps is achieved when Early Token Release
in enabled.
9595 Main Page
|
